What made Japan paralyzed currency interventions?
Oct 31st 2011, A leap in the dark, JPY sell/USD buy intervention.
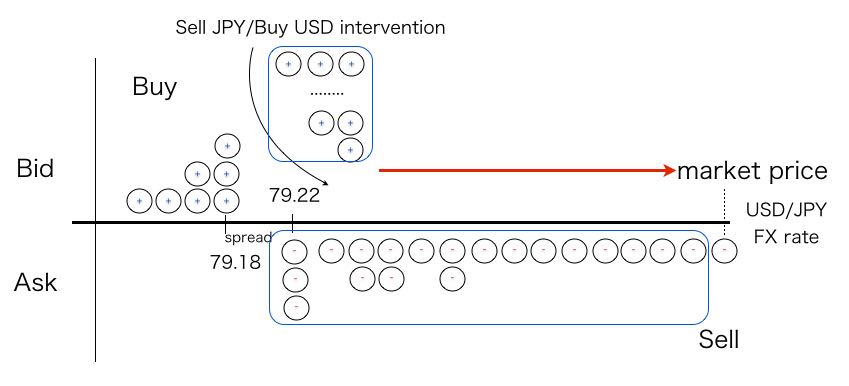
The chart figure1 shows changes of USD/JPY foreign exchange rate at the currency intervention by the Ministry of Finance.
Basically, the government intervenes into FX(foreign exchange) market to operate sell or buy domestic currency for the purpose of correcting FX rate. At this time, the currency intervention changed only 2 JPY(Japanese YEN) in temporary FX rate. It could not effect to shift the FX rate in spite of the scale of intervention cost.(1)
bid price:79.18 Yen
Figure1. USD/JPY foreign exchange rate.
This was the first time such a constant FX rate happened for several hours since float FX market started.
What would happened?
Recently the Japan government sometimes intervened into FX market for JPY sell/USD buy, but there was no effect to change FX rate in a wide range.
Someone insisted the effect of currency intervention was too small to shift in FX rate due to the amounts of transaction per day in FX global market. Another person said the currency intervention was as if it watered in a desert.
Even if the huge amount of transaction is traded per day in FX market, dealers work is day trading. So a trading position is neutral, there is no trading position to move over the next day. Even though trading volume is larger, there is no gap between supply-demand volume to move FX rate in one direction.
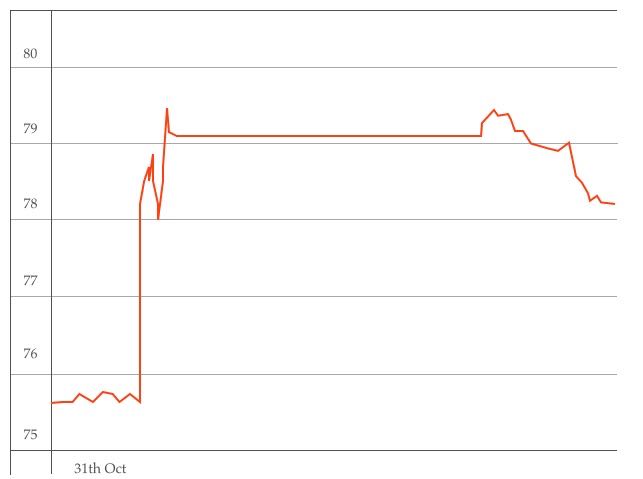
Figure 2 shows a mechanism of bid-ask price determination of FX trading.
Figure2. bid-ask price determination mechanism
The bid-ask orders wait on both sell/buy sides, a trade will close a deal at a market price. The price of the deal is the FX rate.
It is obvious as shown in the figure that the price and the volume must be equated to close the deal. If it places orders of some volume, the trade continues closing a deal of opposite orders which have already placed. Then the FX rate moves to either right or left direction.
Please refer to the chart figure 1 at the currency intervention on Oct 31st, 2011.
The bid price: 79.18 JPY was constant for 4 hours. This status meant that the trade dealt with at the fixed price for 4 hours.
During the trade in this time, the Ministry of Finance put borrowing money, which issued the government short-term bonds for intervention, into FX market in order to change USD/JPY FX rate(2). The Yen sell intervention is ‘a market order’ by the Bank of Japan(BOJ) that will close the positions of opposite orders described as above figure2, then FX rate will shift in right direction to the weak Yen.
The FX rate was constant for the time that the government put the borrowing money into FX market for USD bid orders. This meant someone had already placed opposite orders which the volume corresponded to equal amounts of money of the intervention.
The scale of intervention was ‘9 trillion JPY’. So 9 trillion JPY orders had been placed at the bid price. According to the example described above figure2, someone had placed 9 trillion JPY on ASK side of market price axis as a wall.
In 1997, the law of foreign exchange management amendment was approved, the result of proceeding financial deregulation, everyone can trade currency pairs. It is not necessary to prepare several trillion JPY to place bid orders equal amounts of money for the intervention so that leveraged trading is available.
Equal amounts of money for the intervention have already been placed a bid side to close a deal of the transaction.
They placed orders in the same direction with the Ministry of Finance, then the FX rate shift. When the level in FX rate would come to gain the profit, they would place opposite orders to close the deal by automatic electric trading. The opposite orders which are equal amounts of the intervention would be traded by automatic FX trading. It turned out that was planned to close the deal by the intervention from the beginning.
Figure3 describes JPY sell orders for the purpose of restraining Yen appreciation that will shift the FX rate in right direction to the weak Yen under normal liquidity.
Figure3. Order positions and liquidity in FX market
But the currency intervention closed the deal by opposite orders of the arbitrage transaction that was equal amounts of money of the intervention at bid price 79.18 Yen. As a result of this, the FX rate could not shift in direction to the weak Yen. It was constant. The yen-sell operation by the BOJ finished closing opposite positions at fixed bid price 79.18 JPY. Consequently, the arbitrager swindled intervention money out of the government’s special account of foreign exchange by using the FX transaction. The currency intervention in order to restrain Yen appreciation only transffered money into the private FX trading account. The amounts of transferred money corresponded to a difference in price between the bid price 79.18 JPY of their transaction and an average of purchasing dollar at market prices under normal liquidity.(3)
(1)The currency intervention closed a deal at the fixed bid price 79.18 JPY. The scale of sunk cost of the intervention was 9.1 trillion JPY.
A flat line in the part of FX rate in the figure was the deal at fixed price 79.18 JPY. This closed a deal of bid orders which correspond to the quantity of money of the intervention.
(2)The Ministry of Finance issues the government short-term bonds to raise money for currency intervention.
(3)If the trade closes a deal at market price under normal liquidity, assuming an average of bid price in the market is JPY 90, there is a difference in price between the bid price and the market price, (90-79.18)/79.18 = 0.1366. A difference in price will be 13.66 %.
The quantity of money to transfer by the currency intervention is, 9.1 trillion(JPY) x 0.1366(13.66%), the intervention transferred more than 1 trillion JPY into the private FX trading account which dealt with the arbitrage transaction.
Year 2002~2004, the large-scale currency intervention
The government intervened in the market almost every day during the term.(4)
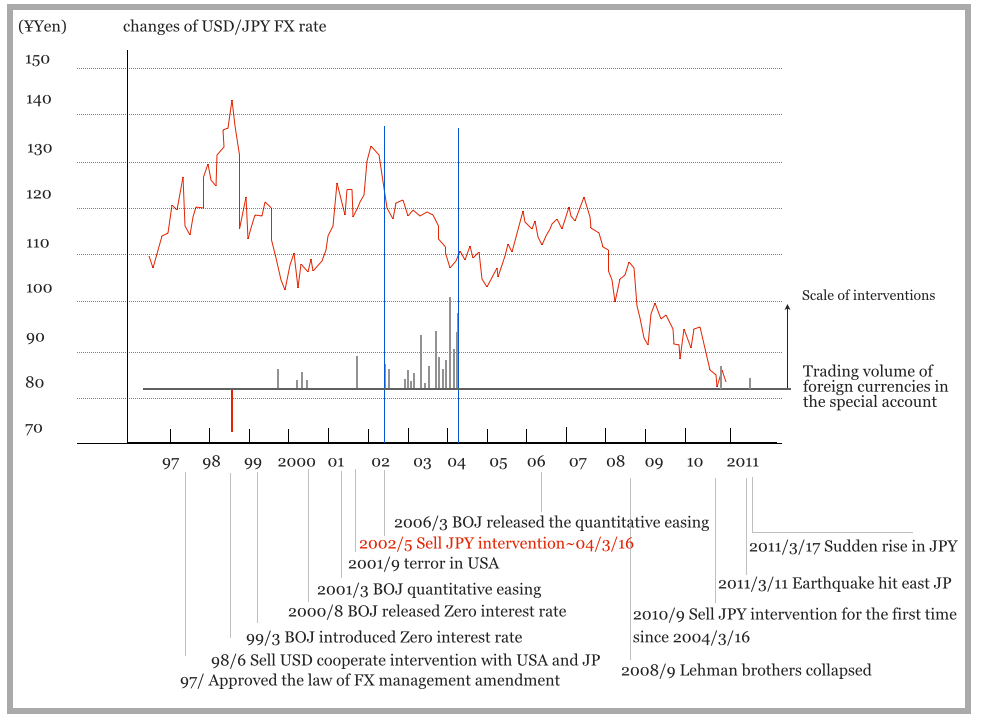
Following figure4 describes the FX rate and scale of intervention in chronological order.
MOF transferred money into the private FX trading account.
Figure4. History of Japan's USD/JPY FX intervention
The currency intervention was effective to correct FX rate as an effective policy until 2001. But there was no effect in FX rate ever since May 2002.
What would happened?
Someone insists scale of intervention is too small to shift FX rate due to a large amount of trading volume per day in FX market.
As described in previous section, the dealer’s trading closes the deal in a day, basically transactions are neutral to adjust their trading position. There is no supply-demand gap for the neutral trading in spite of the sum of the trade that is huge in FX market.
Against this, the amounts of money of the government intervention are so large that the trade closes the opposite positions and it will move bid-ask price in one direction.
Although the sum of trading volume is huge in global FX market, there will be a supply-demand gap of the deal when the government intervenes to the market, because the amounts of money of the intervention are huge. So it will shift the FX rate as shown in figure 3.
In the first place, the intervention would change the FX rate, but it did not during the term. That meant someone had already placed opposite orders of the equal amounts of money for the intervention at the time. This was the same situation of the currency intervention on Oct 31st, 2011 described in the previous section.
An arbitrage transaction was placed as opposite orders at the time of intervention. The intervention did not change FX rate because it closed the deal at the fixed bid price.
Arbitrage transactions had been applied to all interventions during the term.
This indicated someone placed orders of arbitrage transactions on the basis of information of time and volume of the intervention before the government intervened in FX market.
From May 2002 ~ to Mar 2004,(5) the all amount of money for intervention sank in order to close a deal of the arbitrage transaction in spite of its scale because all interventions almost did not effect to shift in FX rate.
The currency intervention gave money to close the positions of opposite orders which had already placed equal amounts of money of the intervention. These operations continued until Mar 16th, 2004.
(4)It was announced that “the government intervened to restrain JPY appreciation by Hedge funds”. JPY appreciation by hedge funds trading, in other words, the BOJ guards the Japan economy against hedge funds, is a fake story. It is a typical illusion about hedge funds in Japan society. Whoever wants to know the whole thing, see the chart of USD/JPY FX rate(figure4). It will turn out that the fraud group made it all up.
If hedge funds purchased JPY in the same amount of the government intervention, they continued to increase JPY exposure in price range 110 Yen, and they held approximate 40 trillion JPY long position. If the hedge funds could not gain the profit due to the intervention by BOJ and would close their deal, they would release 40 trillion Yen exposure. As a result of releasing their positions, it will happen USD/JPY FX rate fall down sharply. In reality, it is obvious there is NOT a sharp fall in USD/JPY FX rate by seeing the chart of the FX rate.
The truth is, internal informers and the fraud group let the Ministry of Finance transfer money into their private FX trading account by using intervention opportunities on the basis(delusion) of BOJ vs hedge funds.(→(6)the False Realities)
*A supplemental explanation
BOJ is as a mediator between the Ministry of Finance and the FX market. the Ministry of Finance is responsible for the policy and decision making about the currency intervention.
(5) May 22th~June 28th: JPY 4.0612 trillion, Jan 15th~Dec 31st 2003: 20.425 trillion JPY, Jan 2nd~Mar 16th 2004: 14.8313 trillion JPY, the record of total 39.2725 trillion JPY intervention were publicly announced.
This was no relation to level or in direction of FX rate. That merely increased dollar reserves. And the interventions transferred the profit to private FX trading accounts.
Mar 18th, 2011, the line connecting the concerted intervention at this time to the massive FX intervention 7 years ago
On Mar 11th, 2011, the earthquake hit east Japan, then the disaster of tsunami took place and the accident of atomic power plant damaged infrastructure system contained supply chain disruption.
A few days later, USD/JPY FX rate rose sharply in the early morning on Mar 17th. The strong Yen demand hit the highest value on record. All market participants regarded this changes as an effect of the earthquake disaster. The Japan government led consensus on concerted intervention into FX market with G7 countries, and the government tried to operate FX rate in a direction to the weak yen.
Some economist explained the sharp rise in USD/JPY FX rate was due to the repatriation of life insurance companies or insurance against damage companies. But the companies denied it which was sufficient domestic reserve. So they did not sell off investment assets in foreign countries and did not return it. Another explanation was investors risk averse. But it is putting the cart before the horse. If investors behave risk averse, the currency will fall down. The earthquake disaster damaged infrastructure system, in the verge of radioactive contamination due to the atomic power plant accident, unstable electric power supply stopped the manufacturing activities. If investors held assets in foreign countries, it was safety do not move it under the circumstance.
It was uncertain which kind of money made a strong Yen demand. The FX rate rose suddenly in a minute very short time span on early morning Mar 17th. So it seemed that same money source placed orders to the strong Yen demand.
The day was same the last date that dealt the transaction of currency intervention arbitrage on Mar 16th, 2004. Just exactly 7 years had passed since the Ministry of Finance transferred money into private FX trading accounts of the fraud group last time. The statute of limitations on a criminal fraud is 7 years in domestic criminal law in Japan. So there was a possibility that the event had been done by the fraud group 7 years ago.
Then the FX market was unstable. It seemed the same fraud group intended to the strong Yen demand, because they dealt large scale arbitrage transaction on last currency intervention Oct 31st, 2011(Figure1). This largest amount of cost for intervention in the past could not effect changes in FX rate, then the cost 9 trillion JPY only traded the opposite orders off which had already placed.
Thus all currency interventions by the Ministry of Finance since 2002 has given opportunities for large scale arbitrage transactions. The amount of giving money comes to the scale of several trillion JPY. It is obvious from the figure of bid-ask spread described in figure 3.The currency intervention, which there was no effect in FX rate, only closes transactions at equal amounts of opposite orders.
The currency intervention by the Japan government cannot effect changes in the FX rate because the fraud group always sets the arbitrage transactions in the FX market at that time.
Policy makers and people in a business community have to recognize the fact of -information leakage about time and amounts of interventions, and the fraud group had dealt with arbitrage transactions by using intervention opportunities.(6) Unless responsible officers reveal the transactions by the fraud group, the currency intervention never effects changes in Japanese Yen FX rate.
The purpose of currency intervention has transformed to make a slush fund ever since 2002 in Japan. This is the reason why currency intervention paralyzed and the economy cannot leap from the long-term depression.
The statute of limitations.
(6) The fraud group placed a new order and a settlement opposite order in advance, then they instructed the BOJ to intervene into the market. Internal informers conspired with the fraud group and they let the Ministry of Finance transfer money into their private FX trading accounts by using intervention opportunities.
It is dark at the foot of a lighthouse. Members of the administrative organization are not always ethical. The fraud group of FX intervention is composed of the smallest units of the administrative organization.
This is a typical case of both 'the Banality of Evil' (Hannah Arendt, [Eichmann in Jerusalem:A Report on the Banality of Evil]) and 'the False Realities' (Karel van Wolferen,[The False Realities Of A Politicized Society]).
*Refer to "THE LUCIFER EFFECT" for the nature of the fraud group and "the Banality of Evil".
(Philip Zimbardo,[THE LUCIFER EFFECT])
*Hyman Minsky pointed out that the economy will come to unstable if this kind of finance increase.(i.e. Ponzi finance)(Hyman P.Minsky,[Can "It" Happen Again? -Essays on Instability and Finance-],etc.)